Retinol is one of the biggest buzzwords in skincare these days, and for good reason: it’s the golden ticket to younger-looking skin. These potent compounds help promote skin cell regeneration, improve elasticity, and even out skin tone — all the benefits of a retinol treatment. So, where do you start if you want to incorporate this into your skincare routine? Luckily for you, I’ve rounded up the five best retinol serums that will have you seeing results in no time. Keep reading for more details about each product.
Retinol vs Retinoids
Let me first start off with what was confusing me a lot. You may have seen “retinol” and “retinoids” used as if they’re the same but they’re not. They’re related to each other but definitely not the same. As I didn’t know this at first either, I thought it would be nice to share a little bit of information on the differences between the two.
Byrdie explains that “Retinoids are vitamin A derivatives that are converted into retinoic acid for use in skincare. ‘Retinoid’ is essentially a basic umbrella term for both over-the-counter retinol and prescription retinoids. Retinoids are antioxidants and have a stellar rep as wrinkle-fighters; they promote collagen growth beneath the skin, diminishing wrinkles over time.”
Retinol is a type of retinoid used mainly in over-the-counter products instead of prescription medications. Although retinol is super effective, according to our experts, it’s different from prescription retinoids on a molecular level. In OTC retinol products, retinol is often combined with other ingredients meant to hydrate and brighten the skin.
The big difference between retinol and retinoid—specifically, prescription retinoid—is strength. Retinols contain a lower concentration of the active retinoic acid ingredient, Prescription retinoids have a much higher concentration of the active ingredient. OTC retinol products are less intense than prescription products and work more gradually. Although these products are gentler on the skin than prescription retinoids, they may contain teeny-tiny amounts of the active ingredient.
Source: Byrdie
Most skin types can tolerate retinol or retinoid but you have to slowly introduce them into your skincare routine. If you’re starting out, using an over-the-counter retinol serum is the best option for a slow introduction. Also make sure to use this in combination with a gentle skincare regime, because you don’t want to irritate the skin. Don’t use a retinol every day when you’re starting out, opt for every three days. If your skin allows it, you can build it up to every other day and eventually to every night.
I would recommend seeing a dermatologist to discuss which one (retinol or retinoids) is the best option for you if you have doubts or don’t know how to properly integrate one of them into your skincare routine. A dermatologist can also help you determine what the best retinol serum for your skin type is, if this is something you’re struggling with too.
5 Best Retinol Serums

1. The Inkey List Retinol – $11
If you think that Retinol has to be expensive, you’re wrong. The Inkey List’s Retinol Serum is an amazing, affordable option on the market. It even won an Allure Best of Beauty Award in 2021. This serum is promising a smoother look of fine lines and wrinkles and the Squalane in it helps cushion the delivery of the retinol while also keeping your skin feeling extra hydrated and soothed.

2. CeraVe Renewing Retinol Serum – $20
Another great, affordable option is the CeraVe Renewing Retinol Serum. The gentle formula is packed with retinol to help smooth fine lines and wrinkles, ceramides to strengthen the skin’s natural barrier, hyaluronic acid to hydrate (my fave ingredient!), and niacinamide to calm the skin.

3. Paula’s Choice Clinical 1% Retinol Treatment – $60
Onto an expensive, but very effective for acne, is this Paula’s Choice Retinol Treatment. This Retinol Treatment helps slough off dead skin cells (preventing pores from getting clogged) and decreases oil production. Moreover, the added vitamin C reduces the appearance of dark spots and acne scars and licorice + oat extracts soothe irritation and inflammation.
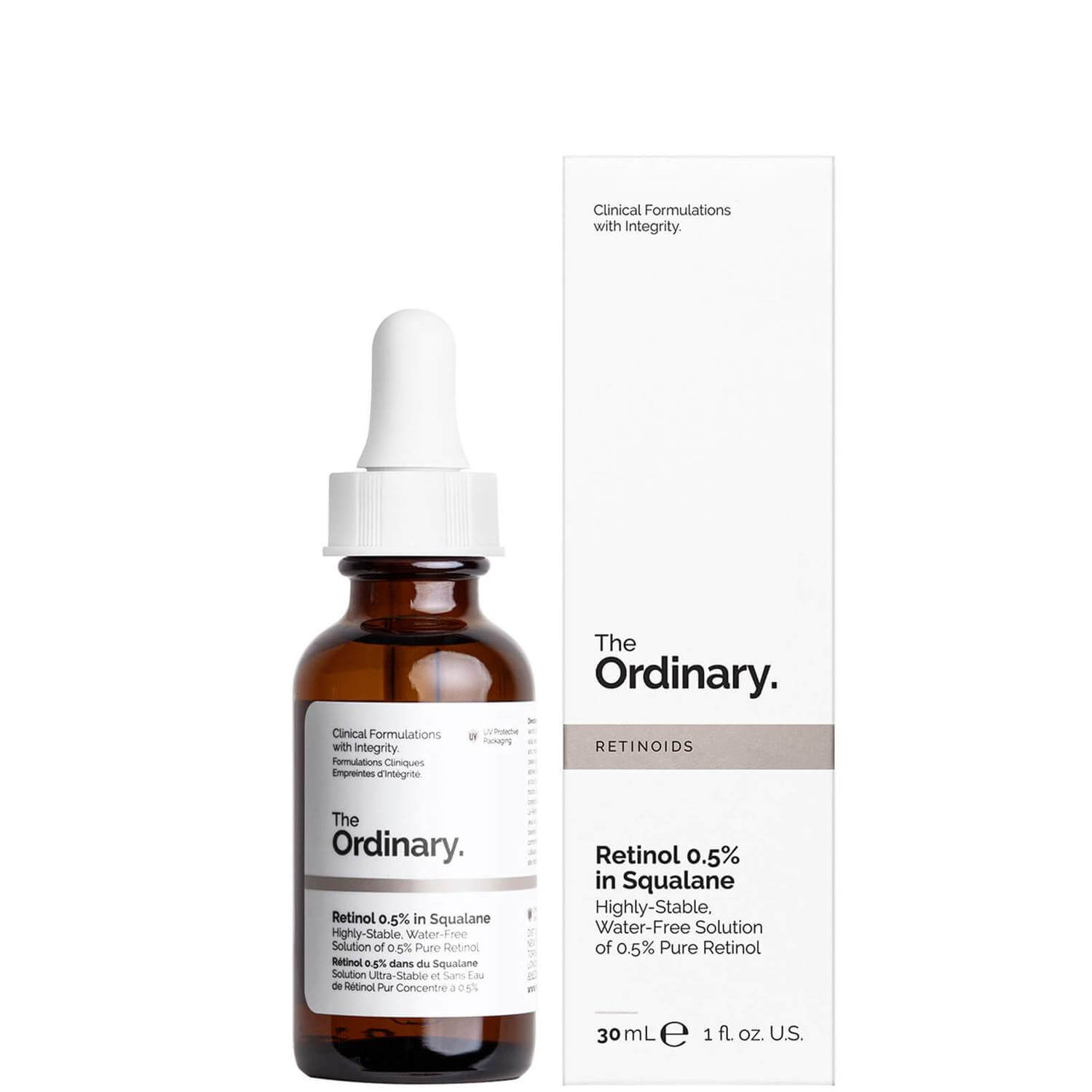
4. The Ordinary Retinol Serum 0.5% in Squalane – $7.50
The Ordinary has quickly gained a cult following for selling effective ingredients at very affordable prices. A powerhouse form of vitamin A, retinol encourages cell turnover, revealing healthier, softer skin while also tackling blemishes, dark spots, and defying signs of aging. Moreover, The Ordinary’s Retinol Serum is water- and silicone-free.
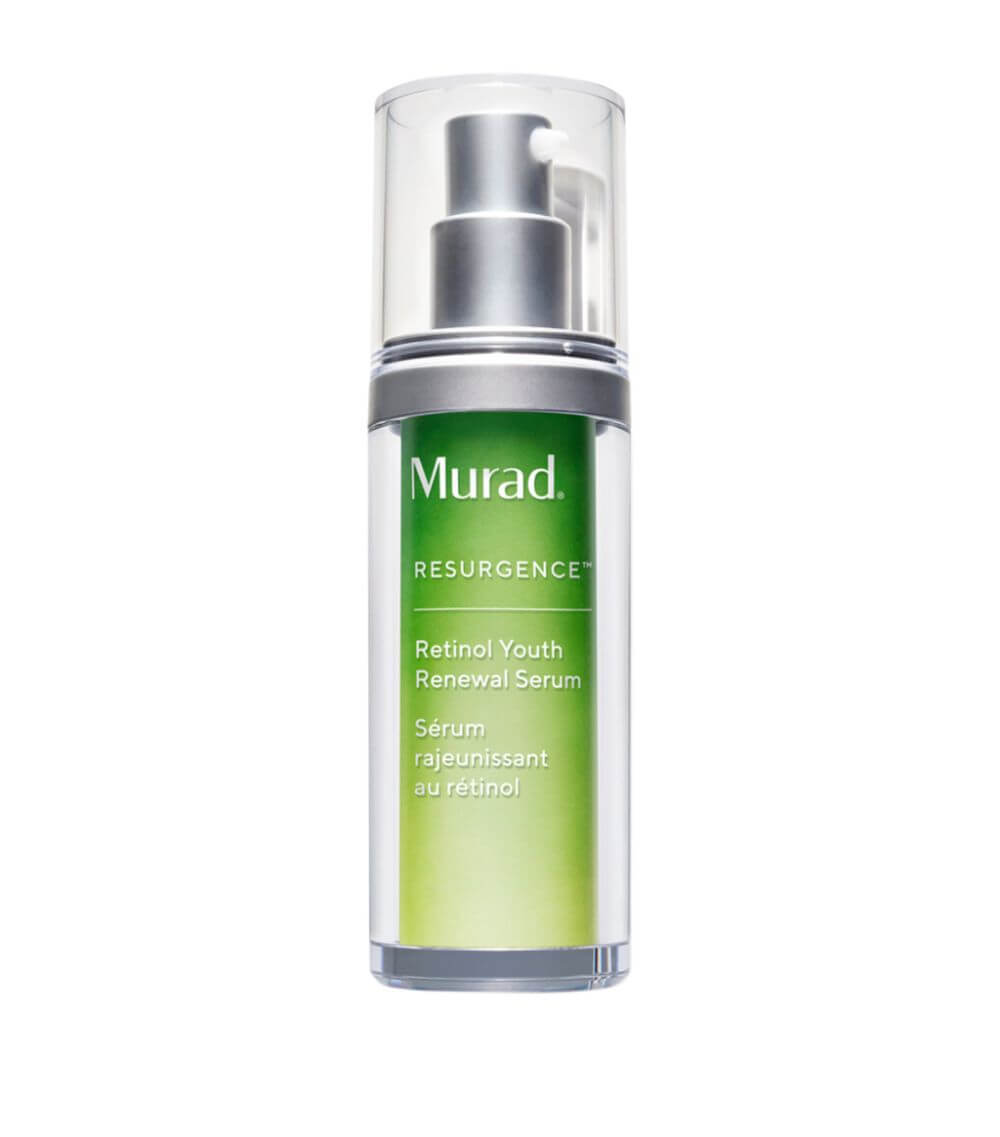

5. Murad Retinol Youth Renewal Serum – $92
Last but not least, an expensive one from Murad. If you suffer from sensitivity, this retinol was formulated with you in mind. Knowing that vitamin A can sometimes cause irritation and dryness in sensitive skins this formula also contains hyaluronic acid to help your skin retain moisture. This way it’s a perfect combination for sensitive skin!
Have you ever tried a Retinol Serum? If so, what’s the best Retinol Serum in your opinion? Let me know in the comments. Also please share your experiences with one of the options I’ve mentioned above, I’m very curious to see if you like them as much as I do.
shop the post