This is a guest post by Marlee from RadiantHer.
Ever wondered what the secret to age-defying, blemish-free skin is? Retinoids and Retinol! These amazing ingredients, derived from Vitamin A, are the holy grail of skincare.
But when it comes to Granactive Retinoid vs Retinol, is one better than the other? We will guide you through the world of retinoids and retinol, compare their effectiveness, and help you choose your skincare regime with the granactive retinoid vs retinol debate.
Granactive Retinoid VS Retinol: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Retinoids and Retinol

Retinoids and retinol, both part of the Vitamin A family, are like the superheroes of skincare, each with a unique power. Retinoids are the powerful ones, with retinol being a milder version of it. Think of retinol as the Robin to the Batman of potent retinoids.
Retinol is the most powerful when it comes to over-the-counter retinoids, packing more punch than others as it can transform into the active form, retinoic acid, providing you with better benefits. That’s why it’s super popular in anti-aging and other skincare products, such as retinol serum, that promote healthy skin cells.
However, if you’re looking for something even more powerful, consider using a potent retinoid for maximum results. When comparing retinoids and retinol, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of each to determine the best option for your skincare needs.
The Science Behind Retinoids and Retinol
There are 6 different classes of retinoids which include:
- tretinoin (all-trans retinoic acid)
- adapalene
- tazarotene
- trifarotene
- alitretinoin
- bexarotene
Retinol esters are found in various skincare products. Retinol, a type of retinoid, needs to go through a two-step transformation to become retinoic acid, while retinyl esters, a gentler version, need three steps to do the same.
Once inside our skin, retinol binds with retinoic acid receptors, converting into retinaldehyde and then into retinoic acid, which actively engages with skin cells. It is this active form of retinoic acid that makes retinol the darling of skincare routines.
Benefits For Your Skin
Retinoids and retinol offer a myriad of benefits for your skin. Studies show[1] that it keeps acne under control, improves psoriasis, and hyperpigmentation. Also, they make acne scars and pores look less noticeable, contributing to firmer skin.
Additionally, retinoids are the magic wand for collagen production. They have multiple benefits for your skin, including:
- Speeding up cell turnover, softening wrinkles, and improving skin tone and texture
- Brightening your skin tone by shedding dead skin cells and speeding up cell turnover
- Helping fade dark spots and hyperpigmentation by increasing cell turnover and slowing down melanin production
So, retinoids and retinol are the go-to solutions for treating breakouts, softening fine lines and wrinkles, and improving skin tone and texture.
Granactive Retinoid: The Next Generation
Let’s now shift our focus to a newcomer – Granactive Retinoid, also known as Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate. This next-generation retinoid is like a high-speed train that gets you to your destination faster and smoother. It’s a faster and gentler version of traditional retinol and offers greater stability.
Advantages Over Traditional Retinol
Why is Granactive Retinoid emerging as a game-changer in skincare? It’s primarily because it activates faster than traditional retinol, immediately getting to work without needing prior skin breakdown.
Second, it’s easier on the skin. Thanks to Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR), a gentler form of retinoid, granactive retinoid is less likely to cause flaking, skin irritation & redness compared to traditional retinol. So, if you have sensitive skin, granactive retinoid is a wonderful choice.
Best Practices For Using Granactive Retinoid
Maximize the effect of Granactive Retinoid by following these steps:
- Cleanse your skin.
- Apply the serum, avoiding the eye area.
- Moisturize.
- Begin by using it every other night and increase the frequency as your skin gets accustomed to it.
You can also mix granactive retinoid with other actives like Vitamin C or alpha arbutin in your skincare routine. Remember, skincare is a marathon, not a sprint. While some changes may be noticeable in a few days, for greater improvement, consistent use for a few months is key.
Retinol: The Classic Choice
Retinol, a long-standing favorite among skincare enthusiasts has been around since the 1930s when it was discovered to be effective for treating acne. Over time, it was found to be beneficial for a lot more, like smoothing skin texture, reducing wrinkles, and boosting collagen, making it popular in anti-aging products.
How Retinol Works on Your Skin
Retinol, a form of retinyl palmitate, activates the cell turnover process in the skin. It gets broken down in the skin into retinaldehyde and then into all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) before the skin can use it.
All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) is shown[2] to have several positive effects on the skin:
- Treats and cures acne, photoaging, and wound healing
- It controls the degradation of cells
- It increases collagen production
By boosting the production of new cells, ramping up collagen and elastin, and causing natural exfoliation, retinol brings about a rejuvenation of the skin.
Tips For Incorporating Retinol Into Your Skincare Regimen
For an effective inclusion of retinol in your skincare routine, begin with a mild retinol and gradually strengthen the dose as your skin acclimatizes. Use retinol products within about three months to ensure their potency.
To apply retinol at night, follow these steps:
- Wash your face and wait for 30 minutes.
- Apply a pea-sized amount of retinol.
- Initially, use it three times a week, and then you can increase the frequency.
- Always apply retinol before or after using a lotion, face cream, oil, or moisturizer.
Granactive Retinoid VS Retinol: A Comparison
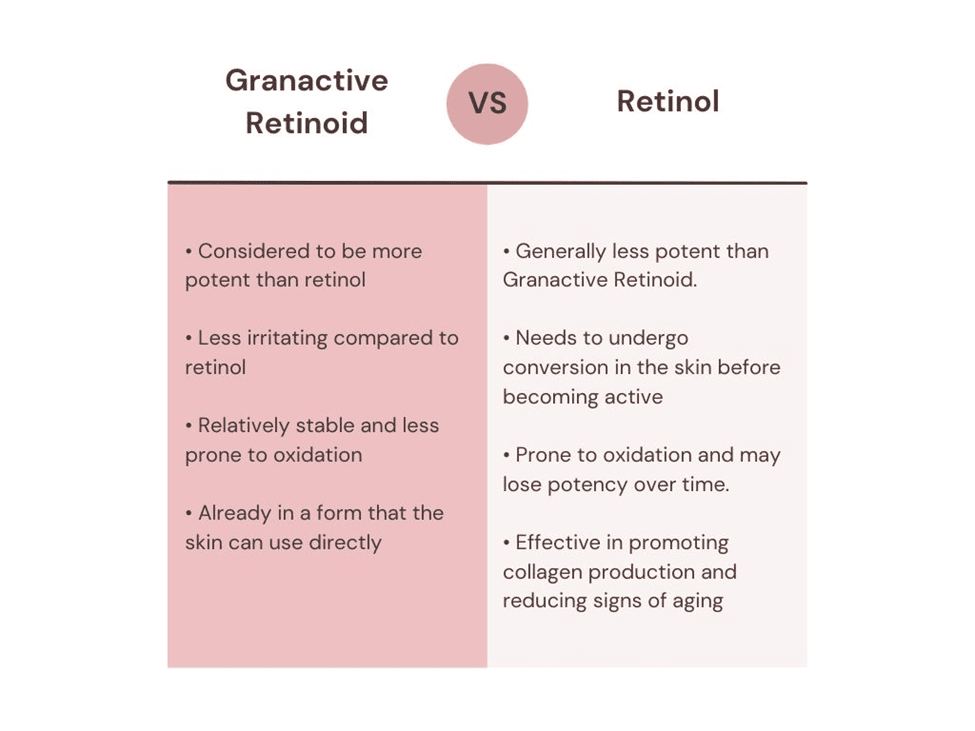
Let’s compare Granactive Retinoid and Retinol closely to understand their differences better.
- Retinol has to go through a conversion process inside the skin
- Granactive retinoid is like a shortcut
- It gets to work faster and better without needing to be broken down.
However, each has its place depending on individual skin types. Granactive Retinoid is designed to be less likely to irritate your skin, while Retinol has a higher chance of causing irritation, peeling, or redness. Also, Granactive Retinoid has a more stable formulation, preventing product breakdown, while retinol can lose its potency, especially when it’s exposed to the sun.
Strength And Effectiveness
Considering strength and effectiveness, Granactive Retinoid is deemed stronger owing to its structural stability. It has been found to be as effective, if not more so, than Retinol for treating signs of aging, wrinkles, and acne.
Granactive Retinoid:
- Is gentler and less irritating to the skin than traditional retinol
- Delivers the desired results
- Retains its power and skincare perks for a longer time, making it more effective in the long haul
Suitability For Different Skin Types
Granactive Retinoid and Retinol can work for all skin types, but their suitability varies. Granactive Retinoid is gentle and works well for all skin types, including sensitive, acne-prone, and mature skin.
Retinol, on the other hand, can cause irritation or dryness in some individuals. However, starting with a gentle retinol and slowly increasing the strength can minimize these effects. For acne-prone skin, retinol can help by clearing up pores, calming down inflammation, and boosting collagen production.
The Role Of Concentration In Retinoid Products

The effectiveness of retinoid products is significantly influenced by their concentration. Over-the-counter retinol products have less of the active retinoic acid compared to prescription retinoids.
When starting with retinoids, it’s best to go for a 0.2% retinol product. However, if you’re just starting out with granactive retinoid, it’s best to go for the lowest concentration. Remember, jumping right into using a strong retinoid product might result in some unpleasant side effects like:
- irritation
- dryness
- redness
- itchiness
- increased sun sensitivity
Choosing The Right Concentration For Your Needs
The appropriate concentration of retinoid products depends on your individual skin type and skincare objectives. For sensitive skin, a lower strength like 0.01% or 0.1% is usually recommended.
For anti-aging, dermatologists suggest using a retinol concentration of 0.25 percent to one percent. If you have acne-prone skin, starting with a lower concentration, like 0.5% or even as low as 0.01%, is advisable. For skin brightening, the amount of retinoid can differ for everyone, and consulting a dermatologist or skincare professional is highly recommended.
How to Gradually Increase Concentration Levels
Initiating retinoids usage:
- Start once or twice a week
- Observe your skin’s reaction
- Begin with a lower concentration, like 0.5 percent
- Consider going higher as your skin gets used to it
You can tell your skin can handle a stronger retinoid if you’re not seeing any flaking, redness, or irritation after using it every night. Signs of tolerance include:
- No peeling
- No dryness
- No redness
- No breakouts from skin purging.
Summary
From understanding the basics of retinoids and retinol, we explored the revolutionary Granactive Retinoid, and classic Retinol. We’ve compared their strengths, effectiveness, and suitability for different skin types, and discussed the importance of choosing the right concentration.
Whether you choose Granactive Retinoid or Retinol, remember, skin health is a marathon, not a sprint. Consistent use, patience, and listening to your skin are the keys to unlocking the potential of these powerhouse ingredients.
About the guest post author: Marlee is the owner of the beauty blog radianther.com, whose passion is to help you feel your absolute best through beauty tips, tricks, and recommendations. She started her beauty journey over 10 years ago and went through extensive testing and researching to only share the best with you. When she’s not immersed in discovering new ways to make you feel beautiful, she’s watching Harry Potter for the millionth time, reading a good mystery thriller, or scrolling through funny cat reels.